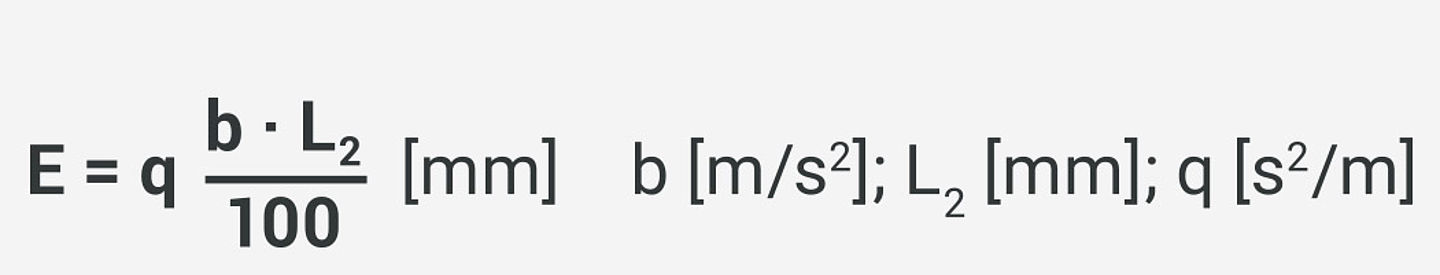High-quality metrology for quality control in the measuring room, production, incoming goods and development.
Gear Metering Pumps & Meter Mix Dispense Machines with highest accuracy for processing liquids and pastes.
High-precision rotary stroke bearings for backlash-free linear and rotational movements for use in machine and device construction.







Permissible accelerations during linear movement
High inertia forces can occur on the ball cage during fast linear movements. During movements that are similar to sinusoidal motions, the mass forces are the highest in the end positions of the linear motion.
The magnitude of the inertia forces is influenced by the following factors:
- Cage material: brass or plastic
- Longitudinal acceleration b
- Cage length L2
- Horizontal or vertical installation position
The required ball contact length E is calculated using the quotient q based on the relationship:
Acceleration b with sinusoidal motion:
The quotient q is specified in the following tables.
The calculated value for E [mm] must be compared with the recommendations in the table. The larger of the two values is used to determine the size of the bearing. The tables contain recommended values for the permissible longitudinal acceleration with ball cage being inside the guide bush at its entire length. These values are average values that can be exceeded, for example, by increasing the preload v.